| Acoustics of the saxophone |
Bb tenor saxophone |
C7 |
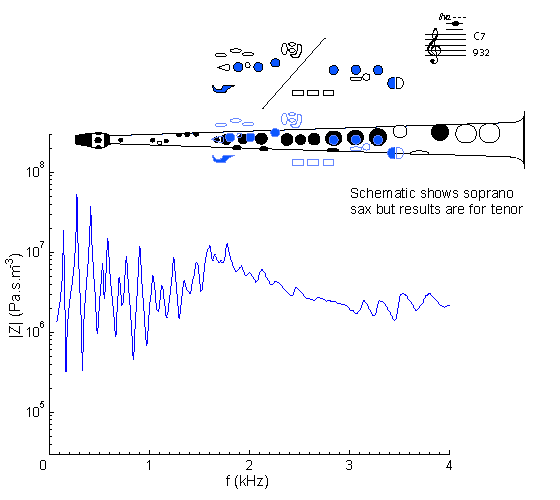
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
This is the sixth note in the altissimo or very high range. The fingering shown here for playing it is the same as that for D#5 and F7. It is not a member of a simple register: it plays at the eight impedance peak.
The weakness of this peak (due to the relatively large cone angle of the saxophone) explains why notes in this range are hard to play and require the player to assist the weak impedance peak of the bore with a strong impedance peak of the vocal tract. See this page for an explanation and some interesting results.
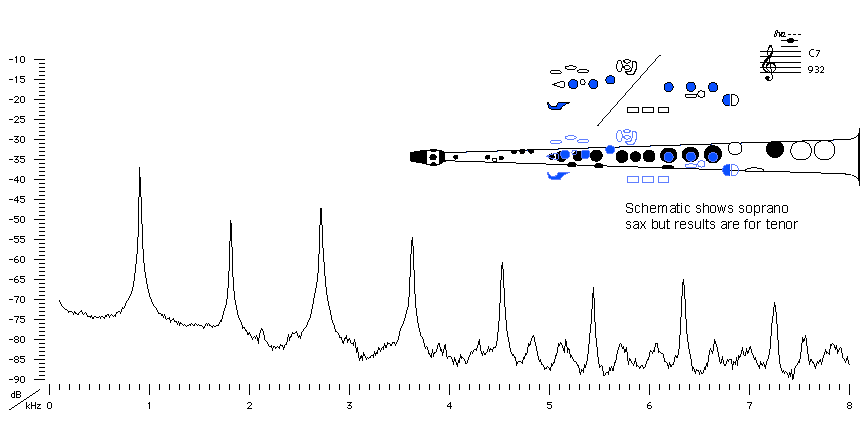
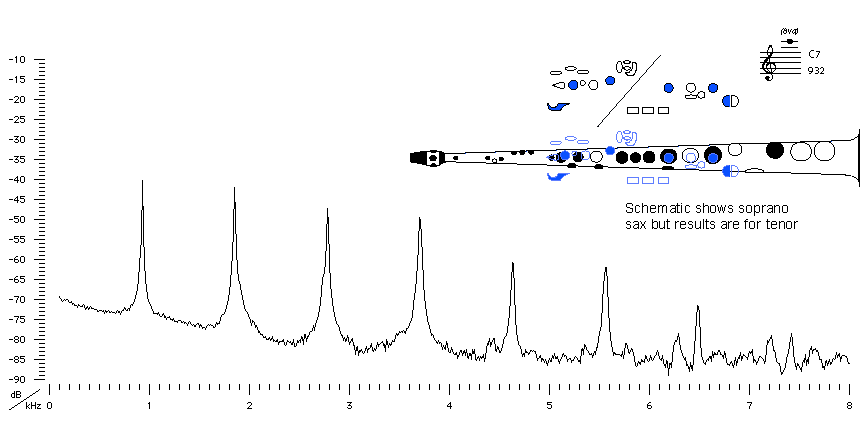
Sound spectrum
of a Bb tenor saxophone
played using fingering for C7.
For more explanation, see
Introduction to saxophone acoustics.
Alternative Fingering |
tenor saxophone |
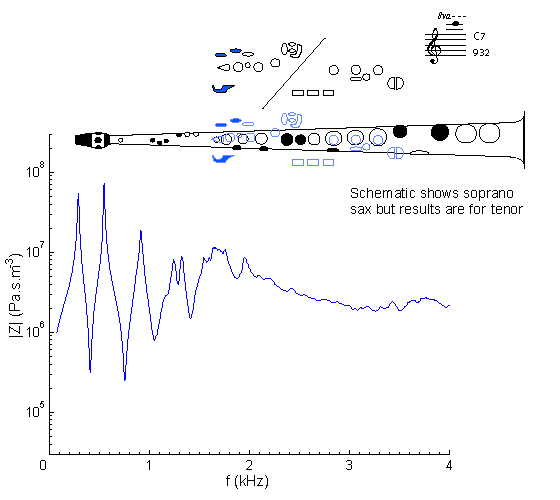 |
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
This is the sixth note in the altissimo or very high range, and plays at the third peak. The weakness of peaks in this range (due to the relatively large cone angle of the saxophone) explains why notes in this range are hard to play and require the player to assist the weak impedance peak of the bore with a strong impedance peak of the vocal tract. See this page for an explanation and some interesting results.
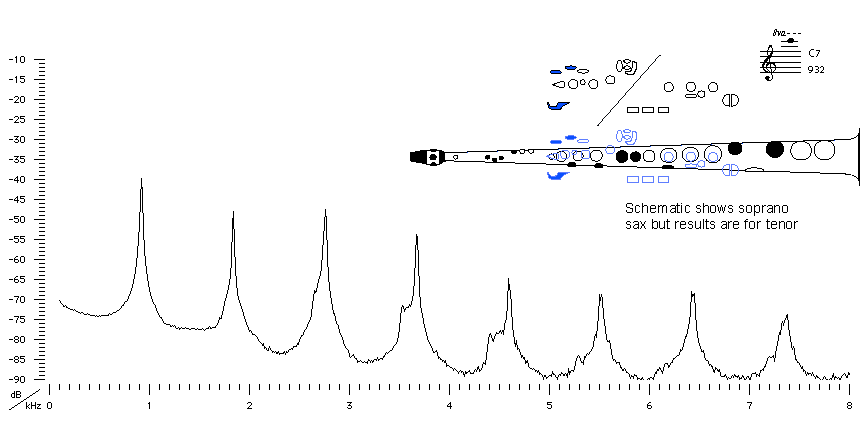
2nd alternative Fingering |
tenor saxophone |
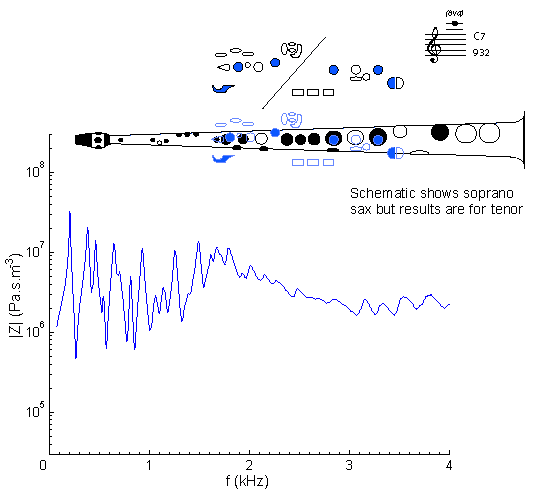 |
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
This is the sixth note in the altissimo or very high range. It is not a member of a simple register: although it plays at the eight impedance peak, few saxophonists (except those discerning ones who have seen this site) would be aware of that. The first few peaks are very strong, and would tend to dominate.
The weakness of this peak (due to the relatively large cone angle of the saxophone) explains why notes in this range are hard to play and require the player to assist the weak impedance peak of the bore with a strong impedance peak of the vocal tract. See this page for an explanation and some interesting results.
|
Contact:
Joe Wolfe
/ J.Wolfe@unsw.edu.au |