| Acoustics of baroque, classical and modern flutes |
modern flute
|
D5 |
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance |
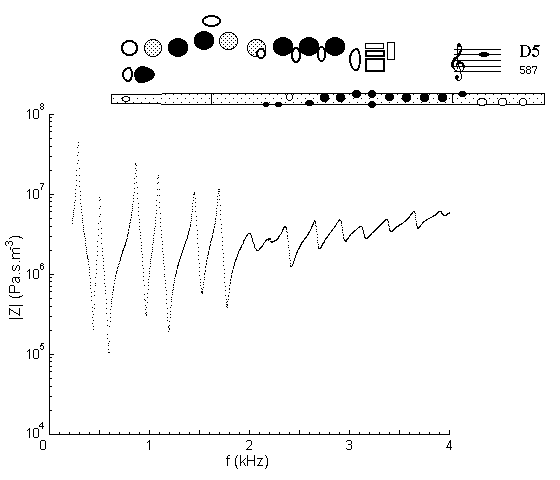
This fingering is comparable to that for D4 except for the open register hole. The register hole weakens and detunes the first resonance. We can also consider that it creates a pressure node (or flow antinode) at the midpoint of the pipe, and thus allows D5 but not D4. Compared with the D4 impedance spectrum, the low frequency minima are less deep and at considerably higher frequency.
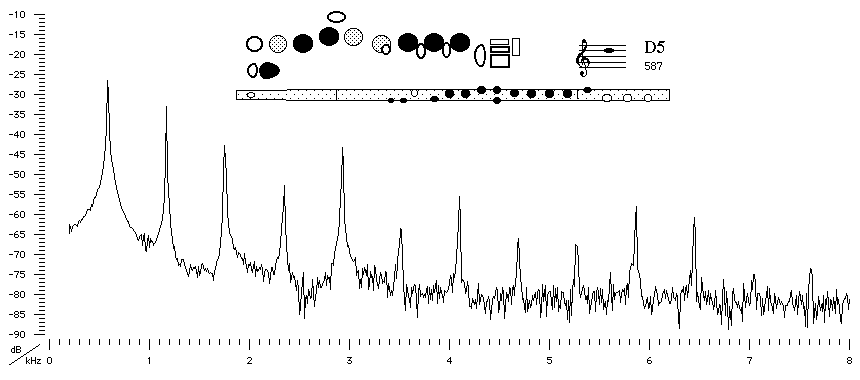
Sound spectrum
of a modern flute with a B foot played using conventional
fingering for D5.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() You can hear D5
played with conventional fingering
by Geoffrey Collins.
You can hear D5
played with conventional fingering
by Geoffrey Collins.
Alternative Fingering |
modern flute B foot |
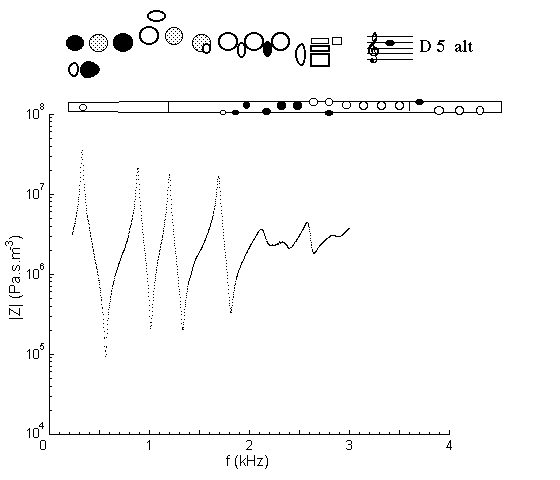
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance |
The open trill key acts as a tone hole for D5 (with cross fingering), and this gives the first minimum in the impedance spectrum. Note that further minima fall at frequencies that have no harmonic relation to this fundamental. Consequently, the sound spectrum shows a fundamental and no visible harmonics, hence the soft 'covered' tone.
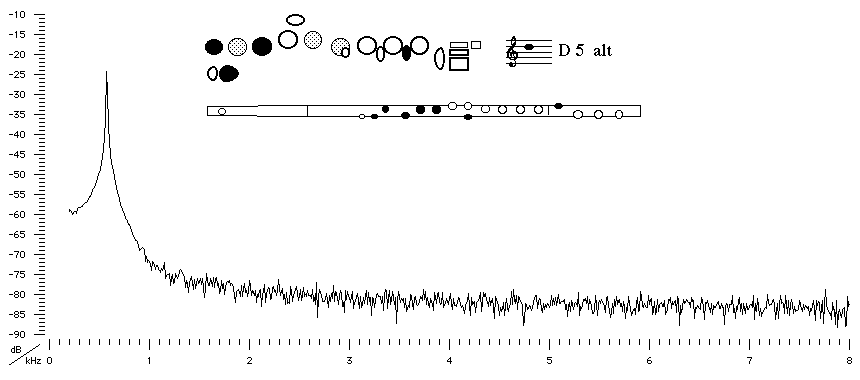
Sound spectrum of a modern flute with a B foot played using alternative
fingering for D5.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() You can hear D5
played with alternative fingering
by Geoffrey Collins.
You can hear D5
played with alternative fingering
by Geoffrey Collins.
| Acoustic measurements are available for these flutes - modern B, modern C, classical C, classical D, classical flared, baroque Sound clips are available for modern B, classical flared and baroque |
To compare flutes, it is easiest to open a separate browser window for each instrument. |