| Acoustics of the clarinet |
Bb clarinet |
C#5 |
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
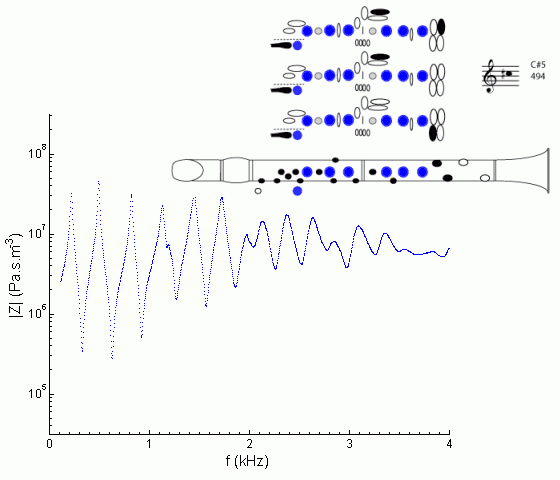
Note how similar this spectrum is to that for F#3. (Of course, the clarinet overblows a 12th.) The only substantial difference is the reduction in the first peak. The purpose of the speaker key is just that: to destroy the fundamental resonance so that the instrument will not 'drop down' to the lower register. See register hole for details.
At frequencies below about 1.1 kHz, this curve looks rather like that for B4 or C5, but raised in frequency because the tube is effectively shorter because of the open tone holes. At higher frequencies, however, the waves propagate past the open tone holes with greater ease, and the situation is more complicated, which gives rise to the irregular shape around 1.2 kHz. (See cut-off frequencies.)
For a general discussion of the clarino register, see the description on B4.
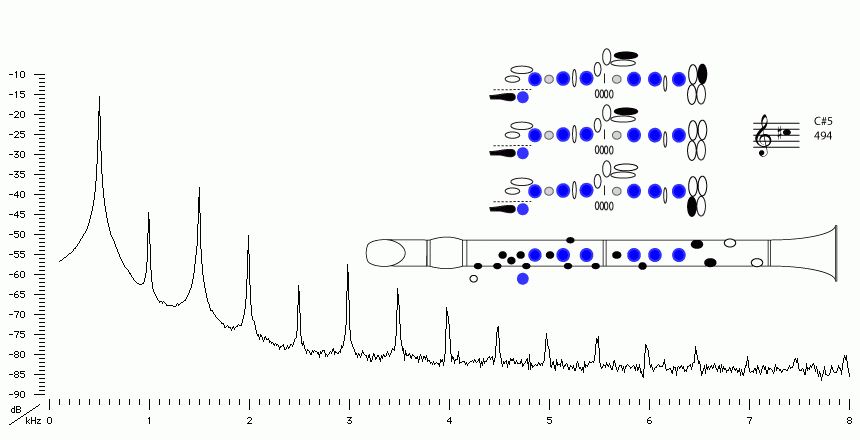
Sound spectrum
of a Bb clarinet
played using fingering for C#5.
For more explanation, see
Introduction to clarinet acoustics
|
Contact:
Joe Wolfe
/ J.Wolfe@unsw.edu.au |