| Acoustics of the saxophone |
Bb tenor saxophone |
A#4 |
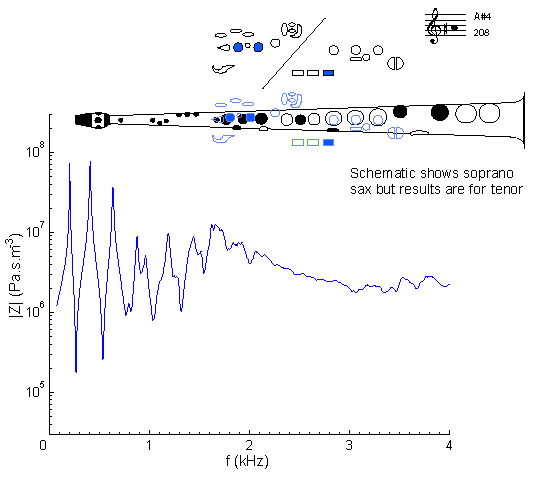
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
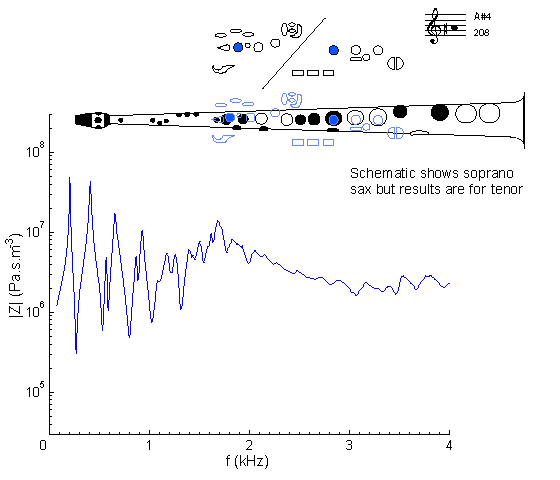
At frequencies below about 1 kHz, this curve looks rather like that for A4, but raised in frequency. At higher frequencies, however, the situation is complicated by the cut-off frequency. Here, the 1 kHz cutoff weakens the third peak. The first peak can be reduced in magnitude and shifted in frequency using a register hole (operated by the octave key): see A#5.
For general comments about the first register, see A#3, which can also play A#4 (and F5, A#5 etc) by bugling. Compare with the impedance spectrum for a soprano sax on written A#4: same fingering but sounding one octave higher.
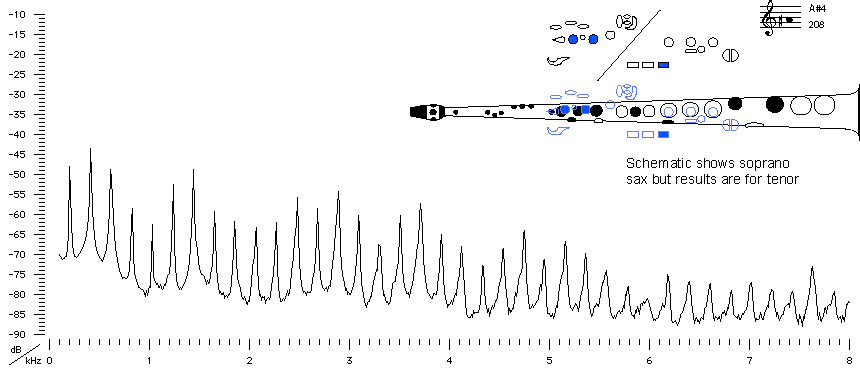
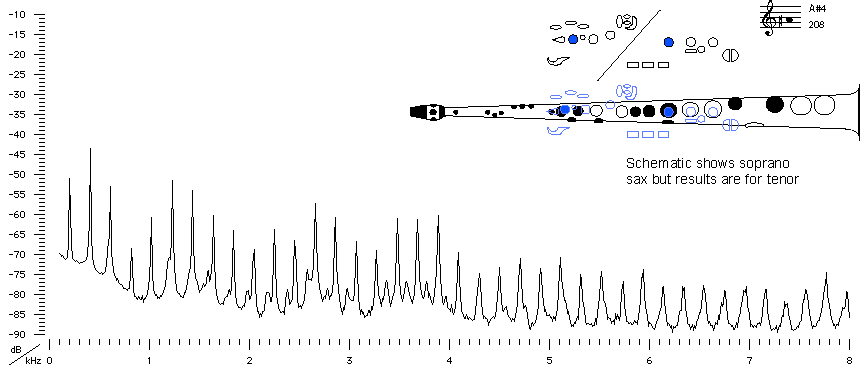
Sound spectrum
of a Bb tenor saxophone
played using fingering for A#4.
For more explanation, see
Introduction to saxophone acoustics.
Alternative Fingering |
tenor saxophone |
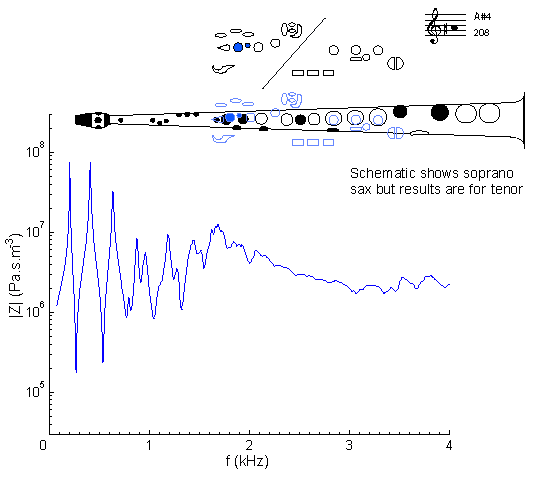 |
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
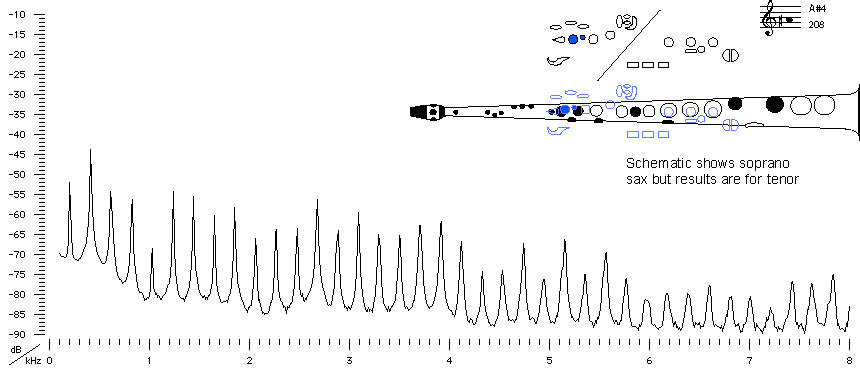
2nd alternative Fingering |
tenor saxophone |
 |
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
|
Contact:
Joe Wolfe
/ J.Wolfe@unsw.edu.au |